Cranial nerves arise directly from the brain in pair formation and connect with the different part of the head, neck and trunk. There are twelve cranial nerves pair, named as per the function or structure. The first two cranial nerves arise from the cerebrum and the other ten cranial nerves begin from the brain stem. Specifically, cranial nerves arise in the below mentioned parts of the brain,
Cerebrum – CN-I The Olfactory nerve.
– CN-II The Optic nerve.
Midbrain-pontine junction – CN-III The Oculomotor nerve.
Midbrain (posterior) – CN-IV The Trochlear nerve.
Pons – CN-V The Trigeminal nerve
Pontine-medulla junction – CN-VI The Abducens nerve.
– CN-VII The Facial nerve.
– CN-VIII The Vestibulocochlear nerve.
Medulla oblongata – posterior to the olive – CN-IX The Glossopharyngeal nerve.
– CN-X The Vagus nerve
– CN-XI The Accessory nerve.
Medulla oblongata – Anterior to the olive – CN-XII The Hypoglossal nerve.
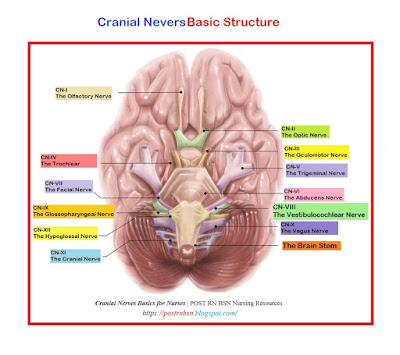 |
| Cranial Nerves Basic Structure |
Cranial nerves have major anatomic and functional differences but they are equivalent to the spinal nerves. Cranial nerves are not spread out at equal distances along with the neuraxis, and have no separation of their dorsal (sensory) and ventral (motor) roots. As a matter of fact, mixed cranial nerves, that is sensory and motor, fibers begin from the brain surface using the same root.
The cranial nerves basically develop the main five senses, the muscles movement for facial expression, control or regulate blood pressure and pulse, digestion and elimination, and most importantly capacity to speak and swallow almost everything. The cranial nerves functions are usually categorized as being either sensory or motor. Sensory nerves are involved with the senses. Motor nerves control the movement and function of muscles or glands.
Each cranial nerve has a Roman numeral from I to XII. This is based off their location from front to back. For instance, the olfactory nerve is closest to the front of head, therefore it is labelled as I.
The 12 cranial nerves named as:
I – The Olfactory nerve
II – The Ophthalmic nerve
III – The Oculomotor nerve
IV – The Trochlear nerve (The longest intracranial length of all the cranial nerves)
V – The Trigeminal nerve
VI – The Abducens nerve
VII – The Facial nerve
VIII – The Acoustic nerve
IX – The Glossopharyngeal nerve
X – The Vagus nerve
XI – The Accessory nerve
XII – The Hypoglossal nerve
POST RN BSN, BSN nursing, BSN, RN to BSN, POST RN BSN, Generic BSN, LUMHS nursing, Post RN BS Nursing, BScN, BSN Past Papers, BSN Nursing notes, nursing, Student nurse, Registered nurse, nurse, LUMHS Post RN BSN Nursing Health Assessment Course Syllabus of First Year First Semester | Cranial Nerves Basics for Nurses
Cranial Nerves Basics for Nurses| POST RN BSN Nursing Resources
















1 Comments
thanks for sharing such kinda post
ReplyDeleteNursing Writing Help